Nvidia Isaac Sim
What Is Isaac Sim?
Isaac Sim is a software platform built from the ground up to support the increasingly roboticized and automated world. The goal is to make it as easy as possible for you to design, tune, train, and deploy autonomous control agents for real, physical robots. [Reference link]
Install Nvidia Isaac Sim on Windows
You can refer to the Nvidia website to install the Isaac Sim platform.
Install Python Requirements
Once you have successfully installed the Isaac Sim platform, you can navigate to the Isaac Sim directory.
For example, my path is D:\Isaac_sim\OMNIVERSE\pkg\isaac-sim-4.1.0.
After entering the Isaac Sim directory, you need to launch the terminal and start the Python development environment that comes with Isaac Sim.
If you encounter dependency issues with packages afterward, you can install the dependencies by following the steps below.
python.bat -m pip install pyads
python.bat -m pip install pyQT5
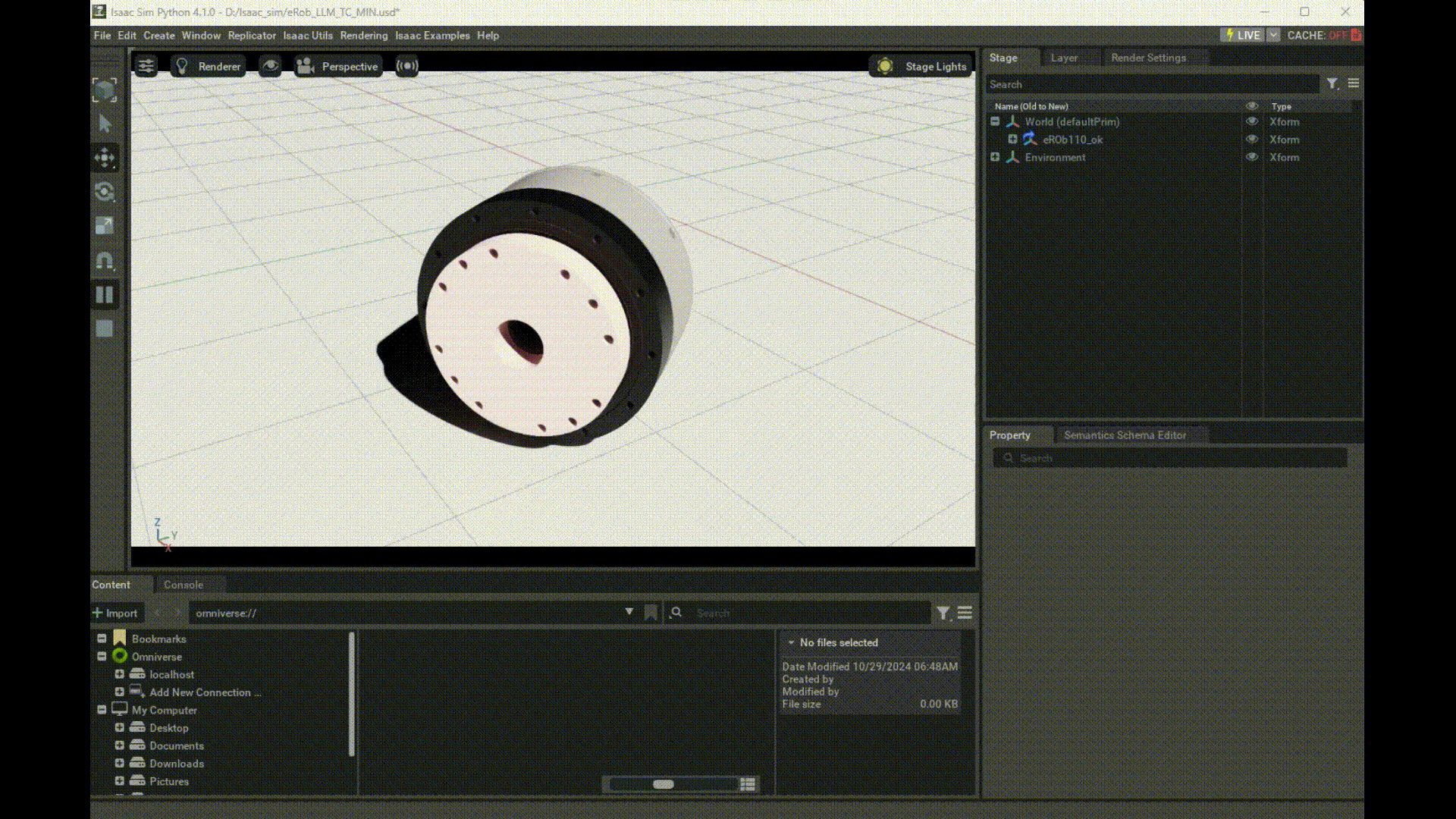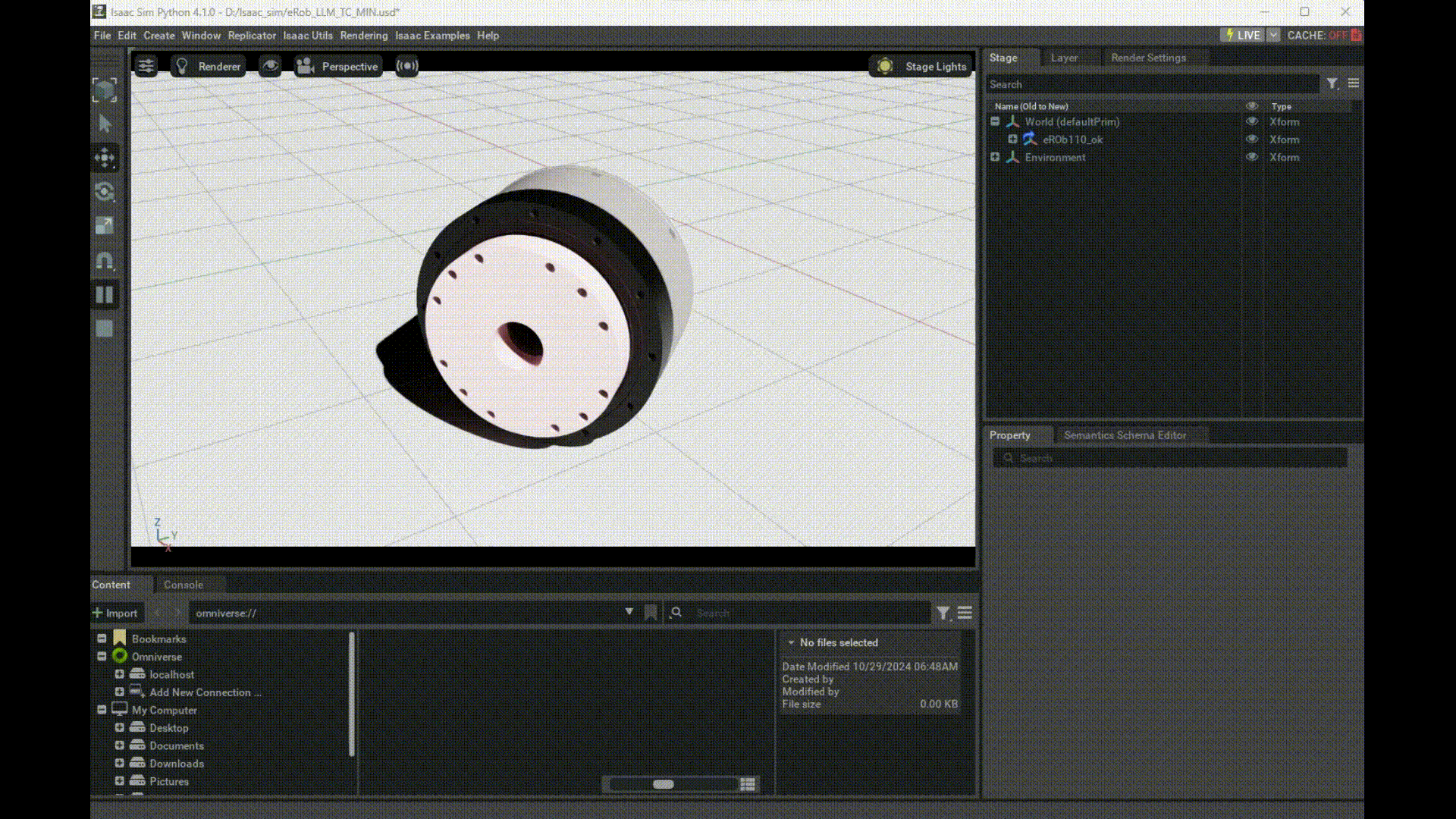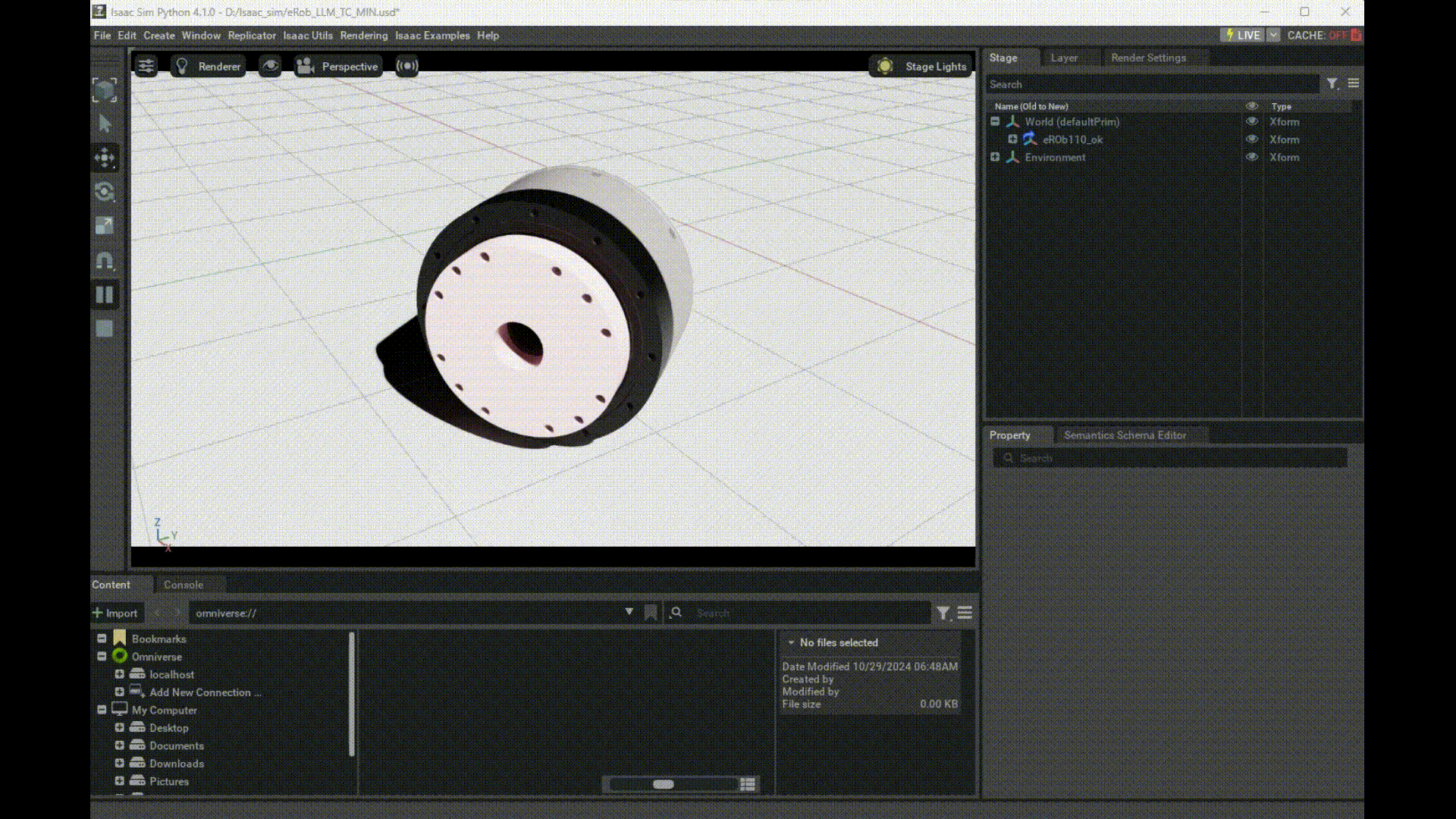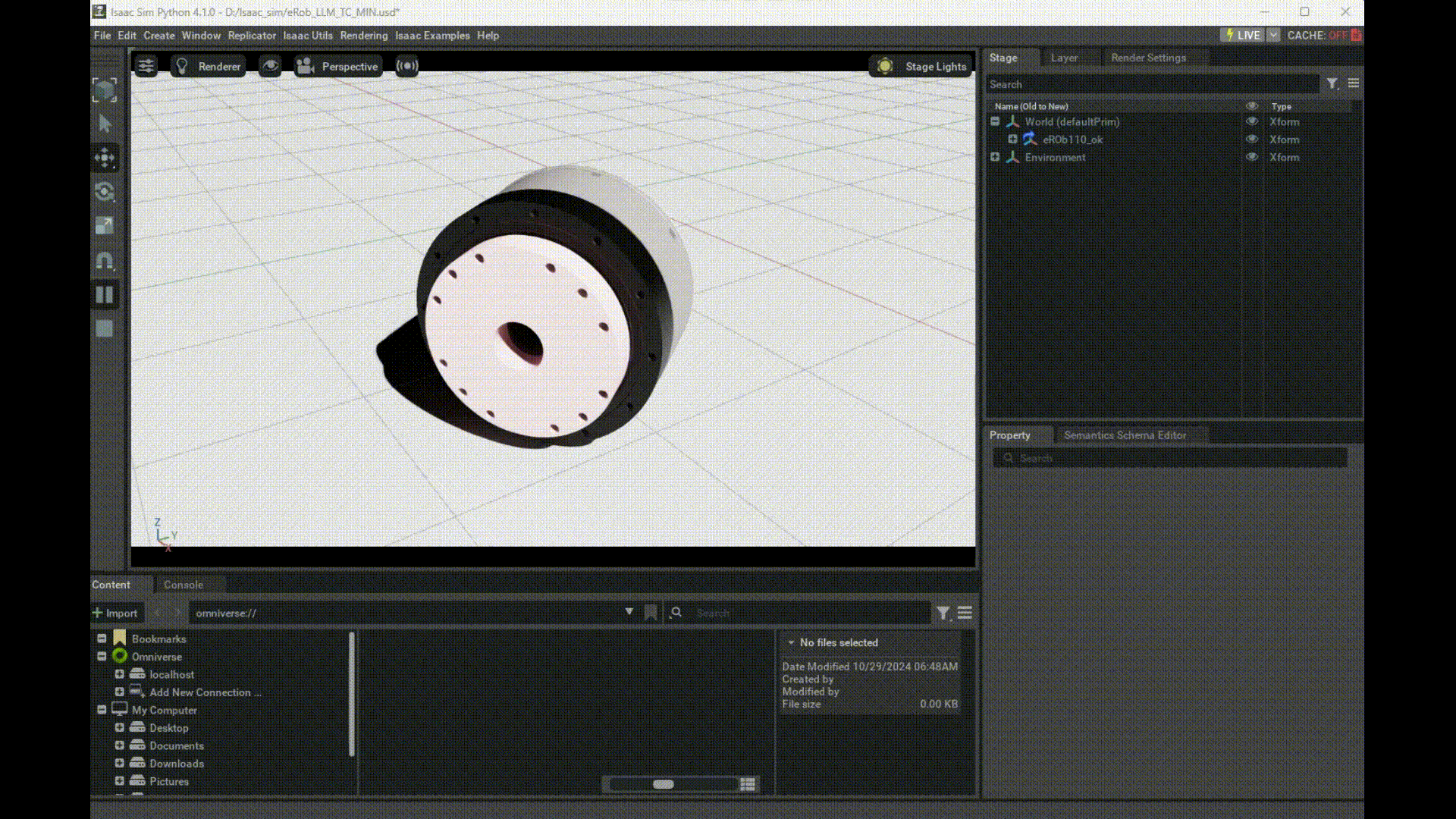
Launching Isaac Sim via Python and Using eRob's Model
Here you can download eRob's usd file and modify the path in your Python code.
# Start Isaac Sim; required for Standalone mode
from omni.isaac.kit import SimulationApp
# Choose whether to run in headless mode
simulation_app = SimulationApp({"headless": False})
# Code execution
print("Simulation started")
# Load an existing scene
from omni.isaac.core.utils.stage import open_stage
#
file_path = "Your usd file path\\eRob_LLM_TC_MIN.usd"
open_stage(usd_path=file_path)
# Add a world
from omni.isaac.core import World
world = World()
# It's recommended by the official documentation to reset the world after adding objects
world.reset()
# Access a specific prim (primitive) at a given path
from omni.isaac.core.utils.prims import get_prim_at_path
prim = get_prim_at_path("/World/eROb110_ok/erob110h_i_SWG2/node_/mesh_/RevoluteJoint")
if not prim.IsValid():
print("Invalid prim")
else:
print("Valid prim")
# Set the target angular velocity for the RevoluteJoint
prim.GetAttribute("drive:angular:physics:targetVelocity").Set(0)
# Method 2: Using get_prim_property() function, with the first parameter as Prim path, and the second as attribute name
from omni.isaac.core.utils.prims import get_prim_property
# Delay function
import time
# Initialize start time
start_time = time.time()
delay_duration = 1.0 # Delay for 1 second
direction = 1
velocity_factor = 0
# Start rendering
while True:
# Retrieve pose and velocity attributes (placeholders)
# position, orientation = my_cube.get_world_pose()
# linear_velocity = my_cube.get_linear_velocity()
# prim = get_prim_at_path("/World/eRob3/Cylinder_01/RevoluteJoint")
# Get current time
current_time = time.time()
# Enable eRob rotation with acceleration and deceleration
if current_time - start_time >= 0.1 and direction == 1:
velocity_factor += 0.1
# Update start_time
start_time = current_time
if current_time - start_time >= 0.1 and direction == -1:
velocity_factor -= 0.1
# Update start_time
start_time = current_time
# Reverse direction if velocity factor reaches threshold
if abs(velocity_factor) >= 5:
direction = -direction
# Set velocity with speed limits
prim.GetAttribute("drive:angular:physics:targetVelocity").Set(velocity_factor * 10.0)
# Retrieve the angular target velocity and print it
angular_targetVelocity = prim.GetAttribute("drive:angular:physics:targetVelocity").Get()
print("drive:angular:physics:targetVelocity:", angular_targetVelocity)
print("\n")
# Step the simulation with rendering enabled
world.step(render=True)